Last updated on April 1st, 2023 at 04:06 pm
What is Digital Thermostat?
Simply speaking, most digital thermostats are conditional switchers that could control the input power supply status of the wired loads.
Considering our products are mainly for industrial and commercial purposes, which require a long-term and constant temperature range, therefore our digital temperature controllers do without the setting option for time spans.
How digital thermostat works?
It’s about the temperature and time, Simply speaking, 3 steps
- Collects the data from the NTC temperature sensor;
- Computing: The inside micro-computer compares it with the pre-set parameters, to get a result;
- Action: Change the power supply status of the corresponding relay if conditions are reached.
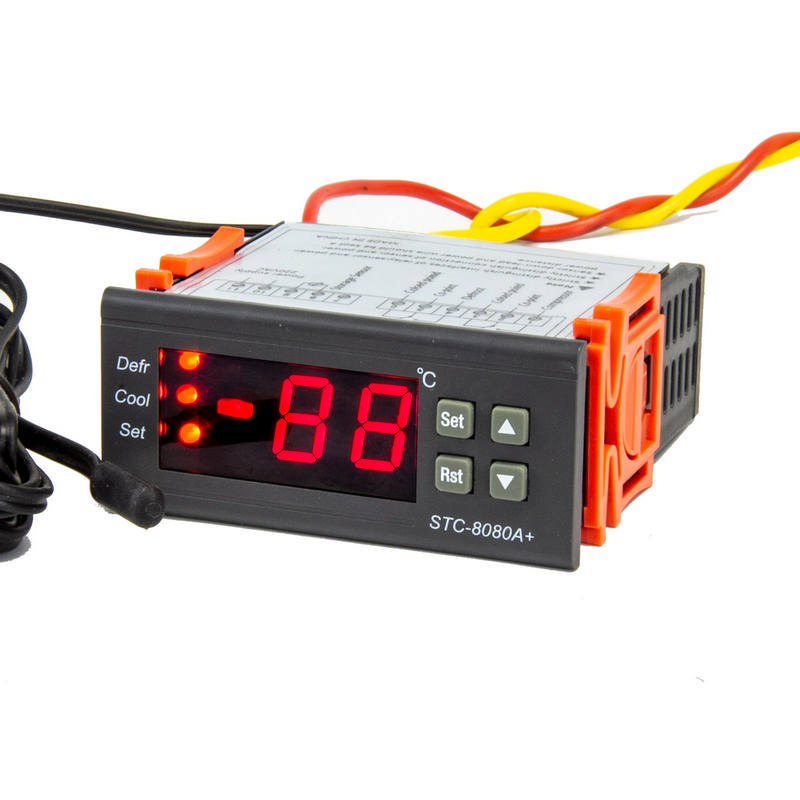
Temperature Conditions
Target Temperature Range
We have to emphasize that a constant temperature actually is a temperature range, not a temperature point; you’ll find that setting up a temperature controller is an easy task once you understand this.
Target temperature Range is the most important parameter of a digital temperature controller no matter it is a programmable thermostat or non-editable.
Assign it mainly through the below methods:
A: SP & Hysteresis

[Temperature set-point] like the position of the boy’s hand, [hysteresis] like the length of the yoyo rope; these two parameters determine the “target temperature range”.
Most thermostats like STC-1000 (STC-1000 Setting video) use bidirectional [hysteresis], but some thermostats may only use unidirectional [hysteresis], please check the product manual.
- One advantage of this design is that it is easy to implement hierarchical management, that is, the administrator can set a limit setting range for the SP to avoid misoperation by ordinary users. Such as the STC-9100 and 9200 controllers.
- Another reason is it is easy to operate for users, especially mounted on display fridges; that is why most of our big panel thermostats for commercial purposes are based on the Set-point method.
Since they are easily misunderstood, once you come across the words “Lower and Upper” or “high and low limit”, take care to see if it’s for the SP or target temperature range, or the alarm temperature range.
B: Only SP
113M PID controller is a special controller,
essentially it’s not an automatic switch, because it’s always on, like a faucet that automatically adjusts the size of the water flow, water flows from the faucet to a bucket which has a Hole in the bottom, and water keeps flowing out. This smart faucet ensures a dynamic balance of water levels, which means keeping around a position or nearly.
Thus, only exists the Set-point which is like the water level position.
Youtube Video of 113M VS STC-1000 temperature controller
C: Lower & Upper Limit
Just like you turn on the map navigation when driving a car, set a starting and an ending; Once the instant room temperature is lower than the [Lower limit Value],
- The relay to the heater powered on;
- The relay to the refrigerator powered off.
on the contrary, once the instant room temperature is higher than the [Upper limit Value],
- The relay to the refrigerator powered on;
- The relay to the heater powered off.
That is why a temperature controller like STC-8080 was called the “High Low Limit Temperature Controller”.
Alarming Temperature
Most digital thermostats within an alert function, mainly visible (the screen shows an error code), or audible (buzzer screams), and some of them exist an output relay to wiring the remote alert.
Once the instant room temperature exceeds the indicated silent range, the controller could alarm to remind people to check the problems as soon as possible, this way reduces the loss.
Like the “target temperature range”, the “safe/silent temperature range” also usually be realized in two methods:
- Assign a high limit and a lower limit temperature value separately;
- Set an “Over-Temp Value“, plus or minus it with other parameters ( e.g. set-point) will get the safe range border.
Time Condition
Time controlling is an important parameter in the digital temperature controller, but it is not like the household thermostat, which often offers multiple time spans that could set different aim temperatures; the time count and control function in our controller mainly for control the loads:
Working Time/Duration
Determine the time of a load lasting working.
Interval Time
Determine the time-space between two loops.
Delay Time
usually exists below types:
- Compressor Delay Time: To protect the loads from start-stop switching frequently, the relay for cooling without electricity before this time over;
- Alarm Delay Time: for example, when summer comes, Your idle freezer is starting to cool again. You know, at the beginning it will cost a long time to low down the room temperature, and you do not want to be alerted by the controller without interruption;
- Fan Delay Time: The compressor just starts, and the temperature of the evaporator is not cold enough, some people do not want the fan to blow hot air into the room; some people want the to fan start earlier than the compressor startup, others like the fan and compressor start and stop simultaneously, all these could be set in the fan delay time.
Other Aspects
Coding/Shortcode Types

En Coding: like our logo, the digital tubes’ shape simulates the English Alphabet “HASWILL”
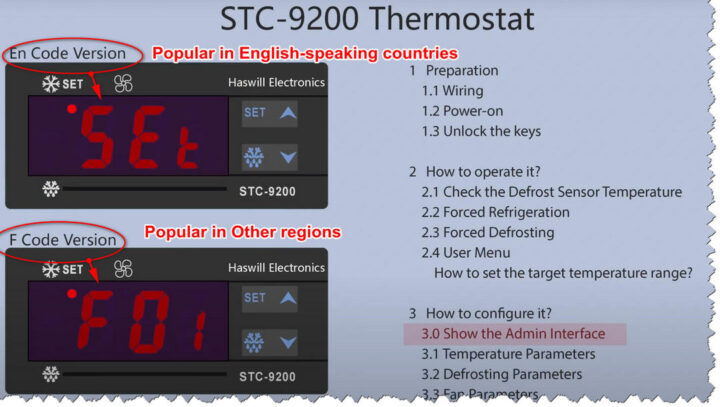
F Coding: Our products mainly adopt the most common coding method: F# as the abbreviation of functions, like F1, F2, and more;
Actually, the above two systems with different visual effects but the functions are totally the same; however, it does not mean the price of these two versions is the same.
More
The above content explained the basic principle of the digital thermostat, When it comes to the production process, more aspects will be involved; e.g.
- the shell material, thickness;
- the front panel size and the mounting dimension;
- the waterproof performance;
- the LED digits refresh rate, Red LED tube or blue or yellow;
- The max current of the relay could bear; the default capacity for single and two relay thermostats usually be 10A; and 8A for controllers which own triple loads; high capacity available to custom products.
- The voltage and temperature unit for different countries/locations;
- The man-machine interactive ways;
- the temperature sampling period and so on.
we can not list all related parameters here, please check it from each product page, and just contact us if you still have a question.
Types of Digital Thermostats
According to the features of different dimensions, we list digital thermostat types as the below four parts, this will help you find the right one quickly.




